Understanding Common 3D Printing Problems: A Comprehensive Troubleshooting Guide
3D printing has revolutionized the way we create and manufacture objects. However, like any technology, it is not without its challenges. This troubleshooting guide for 3D printing aims to help users identify and resolve common issues that may arise during the printing process. 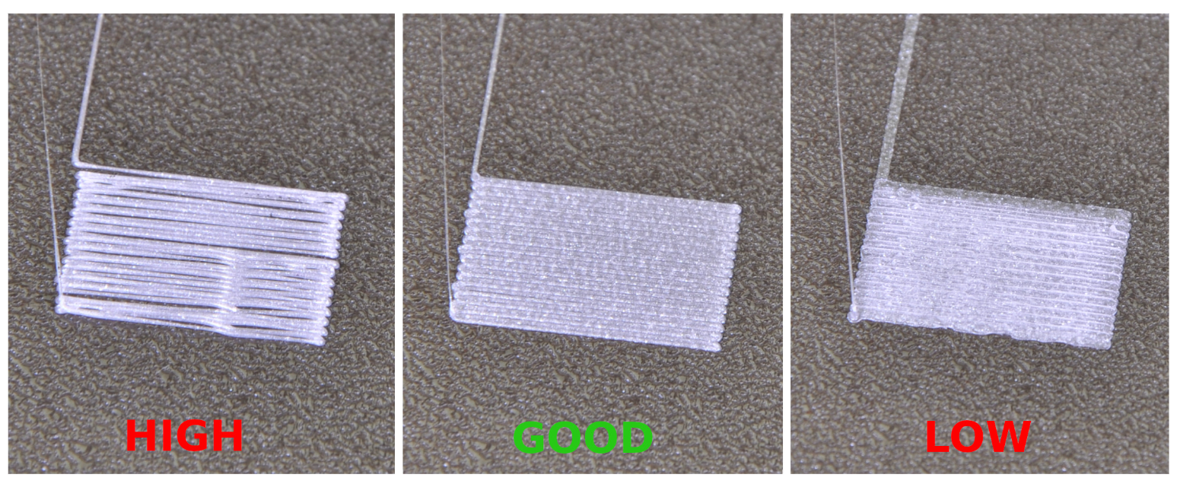
Identifying Common Issues
Before diving into solutions, it is essential to recognize the most frequent problems encountered in 3D printing. Some of these issues include:
- Layer adhesion problems
- Warping of prints
- Stringing and oozing
- Under-extrusion or over-extrusion
Understanding these issues is the first step in utilizing this troubleshooting guide for 3D printing. Each problem can stem from various factors, including printer settings, material quality, and environmental conditions.
Layer Adhesion Problems
Layer adhesion is crucial for the structural integrity of your print. If layers are not sticking together, the print may fail. This issue can often be resolved by adjusting the print temperature. Have you checked if your filament requires a higher temperature for optimal adhesion? Additionally, ensuring that the print bed is clean and properly leveled can significantly improve layer bonding.
Warping of Prints
Warping occurs when the edges of a print lift off the bed, leading to a distorted final product. To combat this, consider using a heated bed, which helps maintain a consistent temperature throughout the print. If you are using materials like ABS, a heated enclosure may also be beneficial. This is a critical point in our troubleshooting guide for 3D printing that many users overlook.
Stringing and Oozing
Stringing happens when small strands of filament are left behind as the print head moves. This can be particularly frustrating. To reduce stringing, you might want to adjust the retraction settings in your slicer software. Increasing the retraction distance or speed can help minimize this issue. Have you also considered lowering the print temperature? Sometimes, a slight decrease can significantly reduce oozing.
Under-Extrusion and Over-Extrusion
Under-extrusion results in gaps in your print, while over-extrusion can lead to blobs and excess material. To address under-extrusion, check the filament diameter and ensure it matches the settings in your slicer. For over-extrusion, adjusting the flow rate can often resolve the issue. This aspect is crucial in our troubleshooting guide for 3D printing as it directly affects print quality.
Conclusion
By following this troubleshooting guide for 3D printing, you can effectively address and resolve common printing issues. For a more detailed exploration of these problems and additional solutions, visit this comprehensive resource. Remember, troubleshooting is an essential skill that enhances your 3D printing experience and leads to better results.
|